TURN-KEY PCB ASSEMBLY: BITTELE ELECTRONICS
PCB MANUFACTURING AND ASSEMBLY
Full Turn-Key PCB Manufacturer
You can quickly get quotes and order PCB fabrication and assembly using our online system. Take advantage of exclusive automatic discounts with our tool. Our BOM pricing tool ensures you receive the lowest price for your order.
START A TURN-KEY PCB ORDER
Benefits and Limitations of Embedded Resistors
Overview of Embedded Resistors
As electronic products continue to evolve toward increased functionality and smaller form factors, embedded components are increasingly adopted to save space on the PCB surface and reduce via holes usage. By integrating components into the internal layers of the PCB, designers can further reduce the overall board size. Today, embedded components especially formed embedded resistors are widely used, offering significant benefits, particularly in signal integrity.
Among various forms, the most widely used and proven technology is thin-film embedded resistors (formed type).
Formed Thin-Film Embedded Resistors
Also known as planar or thin-film resistors, this technology uses a resistive foil laminated with dielectric material. The resistor pattern is defined through PCB etching processes. It is one of the most established and widely adopted embedded resistor technologies. These resistors can be formed on either inner or outer layers of the PCB.
This resistive foil can be laminated with various dielectric materials such as FR-4, polyimide, or PTFE (Teflon), and is also suitable for flex PCBs.
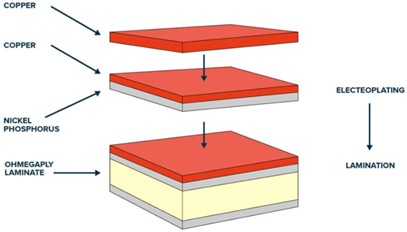
Advantages of Thin-Film Embedded Resistors
1. Reduced Parasitic Effects and Improved Signal Integrity
Embedded resistors can be placed close to signal lines for termination or impedance matching, eliminating the need for additional vias or solder pads. This significantly reduces high-frequency parasitic effects, enhances impedance matching, and minimizes electromagnetic interference (EMI).
See Table 19.2 for parasitic inductance comparisons between 0402 chip resistors and Ohmega embedded resistors.
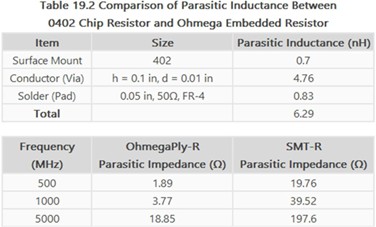
2. Lower Electromagnetic Interference (EMI)
When used in conjunction with embedded capacitors, embedded resistors serve as effective filtering elements to suppress switching noise and EMI.
3. Improved PCB Design Efficiency
By eliminating unnecessary vias and routing, embedded resistors enhance layout flexibility, electrical performance, and thermal management.
4. Enhanced PCBA Reliability
Fewer solder joints and vias improve PCBA reliability. Thin-film resistors also exhibit lower thermal expansion than discrete chip resistors, making them ideal for aerospace application where high G-forces are involved.
5. Cost and Space Savings in High-Density Applications
Since resistors are placed during PCB processing, embedded resistors offer cost savings and space efficiency, particularly in high-resistor-density designs.
Disadvantages of Thin-Film Embedded Resistors
1. Limited High-Resistance Values
Not ideal for applications requiring resistance values exceeding 10 kΩ.
2. Higher Average Cost in Low-Density Designs
In designs with low resistor counts, the unit per cost of embedded resistors is less economical compared to discrete components.
3. Non-Repairable
Embedded resistors cannot be reworked or replaced once fabricated.
4. Tolerance Limitations
Typical post-processing tolerance ranges from ±10% to ±15%. For tighter tolerance requirements, laser trimming is necessary.
For more information about our capabilities or to send us your PCB Design Files for an official quotation, please feel free to Contact Us any time! We can be reached via email at sales@7pcb.com or call at 1-416-800-7540.
Reference: Printed Circuit Handbook (6th Edition, Chinese Revised Version), Chapter 19.
Related Articles:
Please briefly describe the information you are seeking in the search bar below.






 English
English