TURN-KEY PCB ASSEMBLY: BITTELE ELECTRONICS
PCB MANUFACTURING AND ASSEMBLY
Full Turn-Key PCB Manufacturer
You can quickly get quotes and order PCB fabrication and assembly using our online system. Take advantage of exclusive automatic discounts with our tool. Our BOM pricing tool ensures you receive the lowest price for your order.
START A TURN-KEY PCB ORDER
5G Nationwide vs 5G Ultra Wideband
In recent years, the term “5G” has become synonymous with the next generation of wireless technology, promising lightning-fast speeds, lower latency, and the ability to connect more devices simultaneously. But what is 5G ? well, it is a successor of 4th generation internet that offer extreme speed and responsiveness thus called 5g short for 5th generation. Albeit 4G primarily focused on providing faster internet speeds for smartphones, 5G aims to revolutionize multiple industries, including healthcare, transportation, manufacturing, and smart cities.
5G Nationwide vs 5G Ultra Wideband
5G Nationwide and 5G Ultra Wideband are two different types of 5G networks deployed by wireless carriers. While both aim to deliver the benefits of 5G technology, there are notable differences between them. Following points explore the dissimilarities in terms of coverage, speed, and use cases:
Coverage:
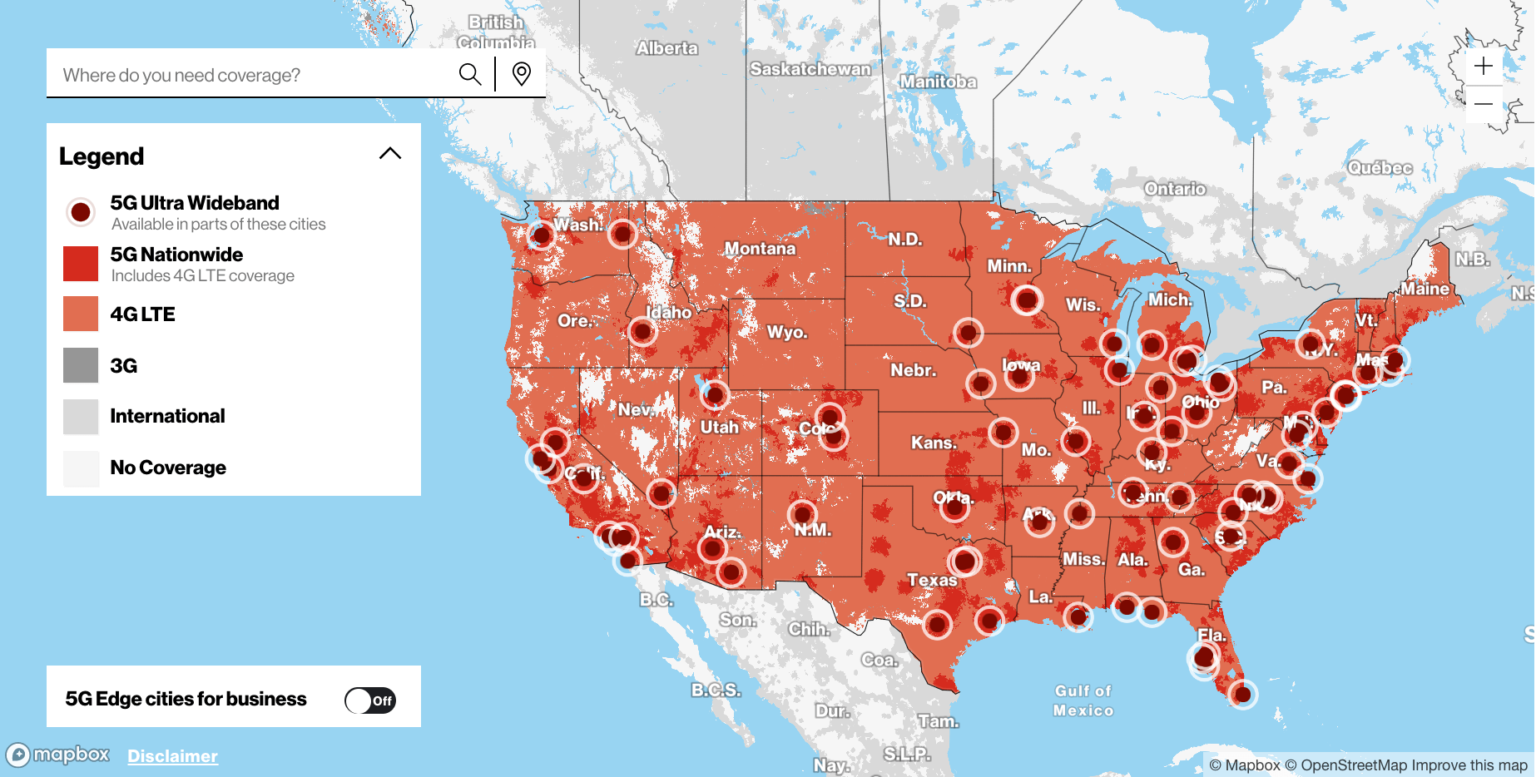
- 5G Nationwide: As the name suggests, 5G Nationwide aims to provide broad coverage across a large geographical area. It utilizes lower-frequency bands, typically below 6 GHz, which offer better signal propagation and can penetrate obstacles like walls and buildings. This type of 5G is designed to provide improved speeds and performance over 4G LTE networks. It offers a more widespread 5G experience, ensuring connectivity in suburban and rural areas where infrastructure deployment is still in progress.
- 5G Ultra Wideband: On the other hand, 5G Ultra Wideband (UWB) focuses on delivering extremely high speeds and low latency in select urban areas. UWB employs higher-frequency bands, often in the millimeter-wave (mmWave) spectrum, which enables faster data transfer rates. However, mmWave signals have shorter range and are more easily obstructed by obstacles, requiring more infrastructure deployment to ensure consistent coverage. As a result, 5G Ultra Wideband is typically deployed in densely populated areas, stadiums, and other high-traffic locations.
Speed and Performance:
-
5G Nationwide: While 5G Nationwide offers an improvement over 4G LTE, the speeds may not be as fast as those achievable with 5G Ultra Wideband. Users can expect faster download and upload speeds compared to 4G, enabling smoother streaming, quicker file transfers, and improved browsing experiences. However, the speeds may vary depending on factors like network congestion, signal strength, and distance from the cell tower.
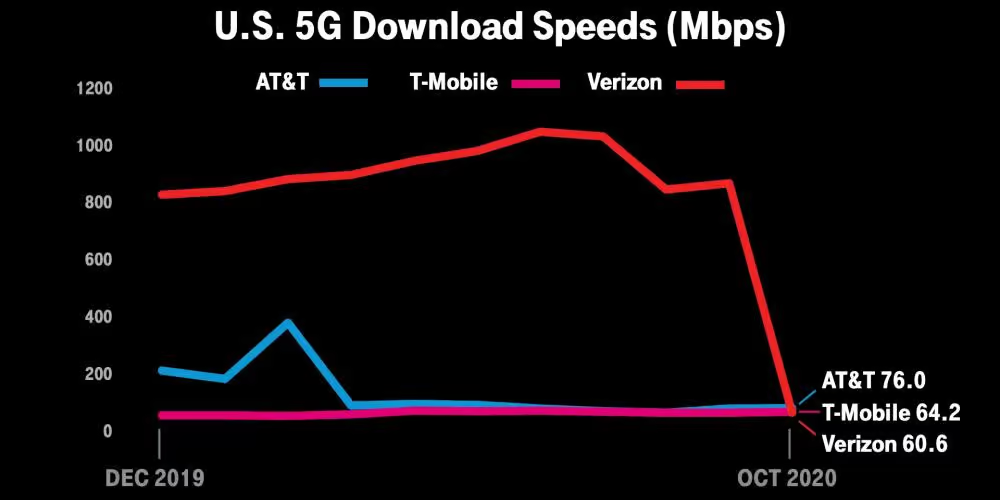
Figure 2. 5g nation wide speed comparison between different carriers -
G Ultra Wideband: 5G Ultra Wideband is designed to provide blazing-fast speeds and extremely low latency. With its utilization of high-frequency mmWave bands, it has the potential to deliver multi-gigabit speeds. This makes it suitable for bandwidth-intensive applications like 4K/8K video streaming, virtual reality (VR), augmented reality (AR), and gaming. 5G UWB's low latency also enables real-time responsiveness, supporting applications such as autonomous vehicles and remote surgeries.
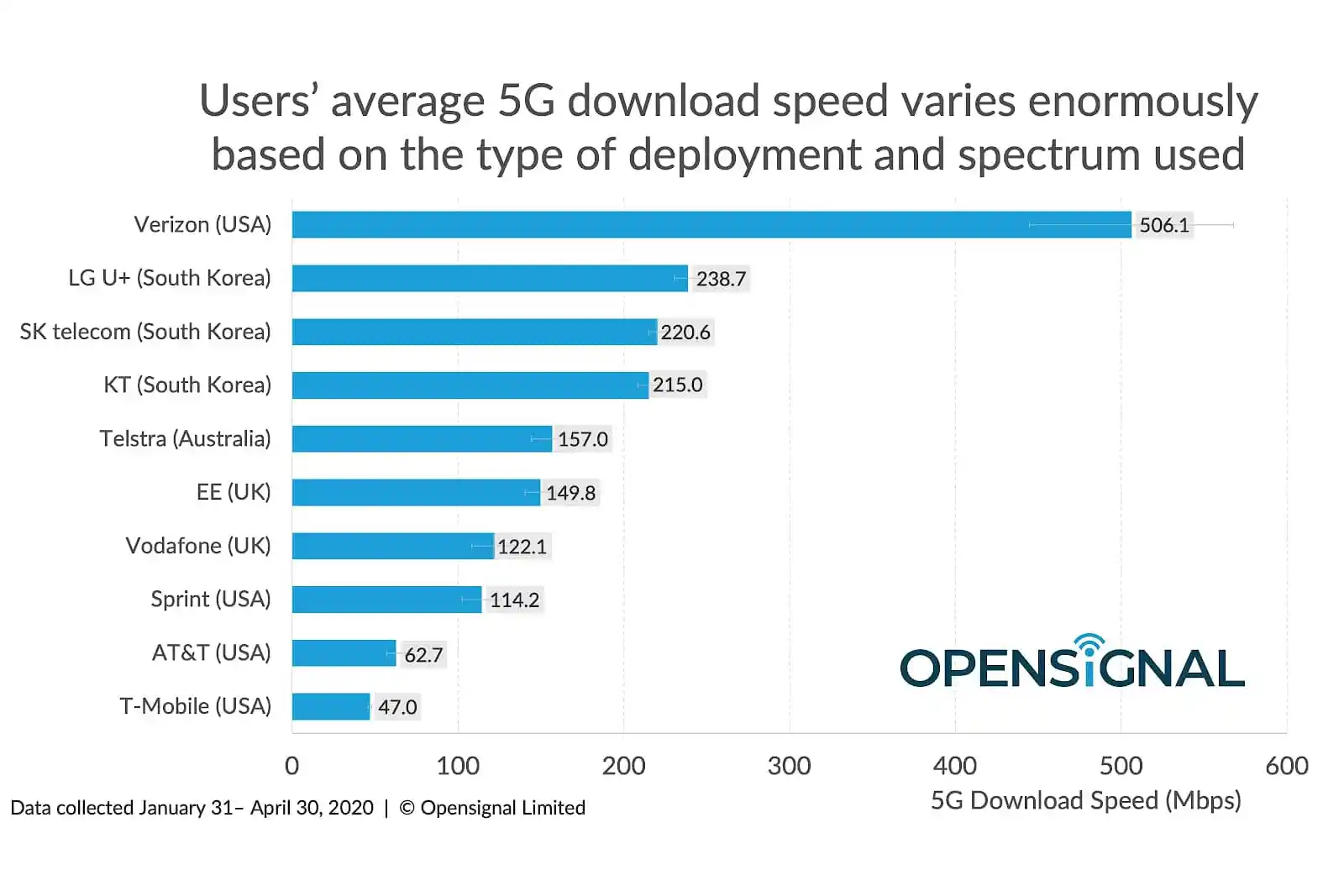
Figure 3. Varation in 5G speed
Use Cases:
- 5G Nationwide: The widespread coverage and improved speeds of 5G Nationwide make it beneficial for a variety of use cases. It enhances mobile broadband experiences, enabling faster web browsing, video streaming, and app downloads on smartphones and other devices. It also supports the growth of IoT devices and applications, facilitating connected homes, smart cities, and industrial automation.
- 5G Ultra Wideband:: The high speeds and low latency of 5G Ultra Wideband open up possibilities for transformative applications. Its capacity to handle massive data transfer rates enables immersive experiences in VR and AR. It also facilitates the development of smart city infrastructure, autonomous vehicles, and advanced industrial automation. However, due to the limited coverage, the availability of 5G Ultra Wideband may be limited to specific locations within cities.
In essence, while 5G Nationwide offers broader coverage and improved speeds compared to 4G LTE, 5G Ultra Wideband focuses on delivering extremely high speeds and low latency in select urban areas. The choice between the two depends on individual needs, with 5G Nationwide being more widely accessible and 5G Ultra Wideband providing exceptional performance in specific locations.
Other types of 5G
- Sub-6 GHz: This type of 5G operates on frequencies below 6 gigahertz (GHz). It provides a wide coverage area and can penetrate obstacles such as walls and buildings. Sub-6 GHz 5G offers a noticeable improvement over 4G but doesn't reach the highest speeds that 5G is capable of delivering.
- mmWave (millimeter-wave): This type of 5G operates on high-frequency bands between 24 and 100 GHz. mmWave offers incredible speeds and low latency, making it ideal for applications that require ultra-fast data transfer, such as virtual reality (VR), augmented reality (AR), and autonomous vehicles. However, mmWave signals have limited range and can be easily obstructed by obstacles.
Working mechanism of 5th generation network
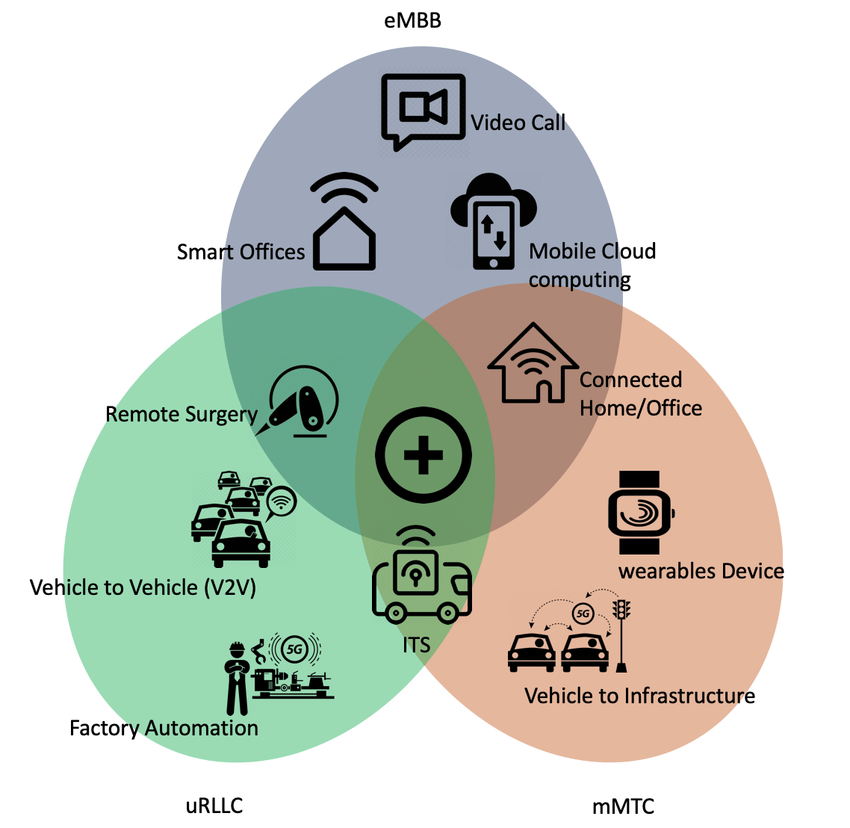
At its core, 5G utilizes a combination of three key technologies: enhanced mobile broadband (eMBB), ultra-reliable low-latency communication (URLLC), and massive machine-type communication (mMTC).
- Enhanced Mobile Broadband (eMBB): eMBB is the aspect of 5G that provides faster internet speeds and greater capacity for data-intensive applications. It achieves this through wider bandwidth channels, higher-frequency spectrum, and advanced antenna technologies. eMBB allows users to download and upload data at significantly higher speeds, enabling seamless streaming, high-quality video calls, and faster file transfers.
- Ultra-Reliable Low-Latency Communication (URLLC): URLLC focuses on delivering near-instantaneous communication with ultra-low latency, ensuring minimal delay between sending and receiving data. This is crucial for applications like autonomous vehicles, remote surgery, and industrial automation, where real-time responsiveness is vital. 5G achieves low latency by reducing network congestion, optimizing transmission protocols, and employing edge computing.
- Massive Machine-Type Communication (mMTC): mMTC enables the connectivity of a massive number of devices, ranging from sensors and wearables to Internet of Things (IoT) devices. 5G provides enhanced support for mMTC by optimizing power consumption, improving device density, and implementing advanced signaling techniques. This allows for seamless connectivity and efficient data exchange among a vast array of devices, opening up opportunities for smart cities, smart grids, and industrial IoT applications.
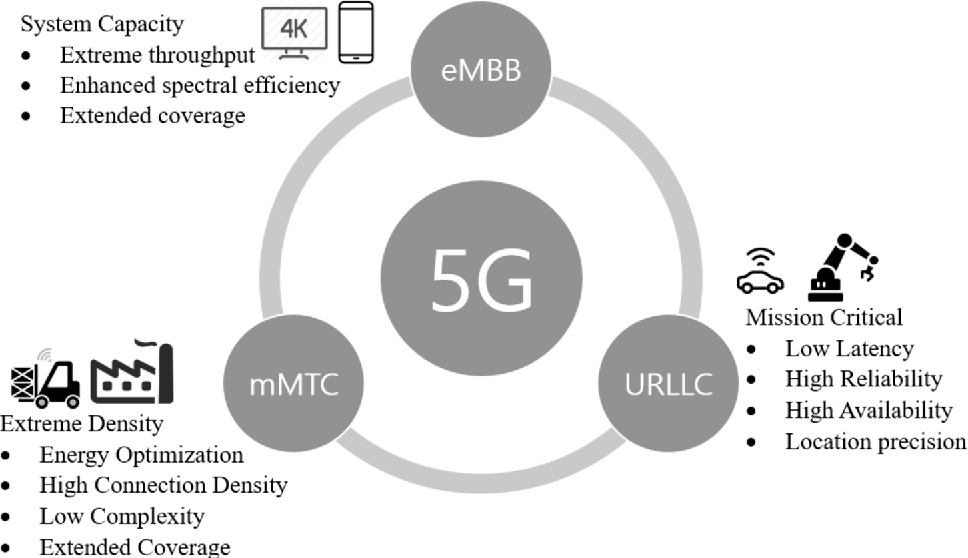
In short, 5G represents a significant leap forward in wireless technology, offering faster speeds, lower latency, and increased capacity. With its various types, but Regardless of the type, 5G networks rely on key technologies like enhanced mobile broadband (eMBB), ultra-reliable low-latency communication (URLLC), and massive machine-type communication (mMTC). These technologies work together to provide faster speeds, real-time responsiveness, and seamless connectivity among a vast array of devices.
As 5G continues to evolve and expand, it has the potential to revolutionize various industries, including healthcare, transportation, manufacturing, and smart cities. By enabling faster and more reliable connections, 5G paves the way for a more connected and technologically advanced future.
Related Articles:
Please briefly describe the information you are seeking in the search bar below.






 English
English