TURN-KEY PCB ASSEMBLY: BITTELE ELECTRONICS
PCB MANUFACTURING AND ASSEMBLY
Full Turn-Key PCB Manufacturer
You can quickly get quotes and order PCB fabrication and assembly using our online system. Take advantage of exclusive automatic discounts with our tool. Our BOM pricing tool ensures you receive the lowest price for your order.
START A TURN-KEY PCB ORDER
How the modern solder reflow oven works?
To successfully solder surface mount components to a circuit board, the heat should be transferred to the solder alloy paste until its temperature reaches a molten point (217°C for SAC305 lead free solder). The liquid alloy will merge with PCB copper pads and become a eutectic alloy mixture. A solid solder joint will be formed after it cools down below molten point.
There are three ways to transfer heat from heat source to heated objects.
- Conduction: Thermal conduction directly transmits through a substance when there is a difference of temperature between adjoining regions, without movement of the material. It occurs when two objects at different temperatures are in contact with one another other. Heat flows from the warmer to the cooler object until they are both at the same temperature.
- Radiation: Heat transfer through radiation takes place in form of electromagnetic waves mainly in the infrared region. Radiation is a method of heat transfer that does not rely upon any contact between the heat source and the heated object. The limitation of radiation is that black body will absorb more heat than white body.
- Convection: Heat convection is the transfer of heat from one place to another by the movement of fluids such as air or vapour gas. It is also a contactless method to transfer heat as well.
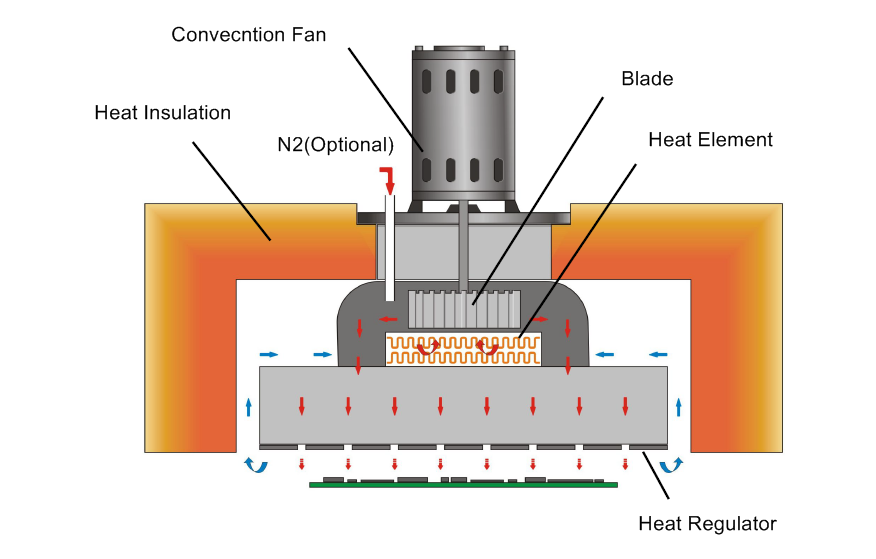
The modern solder reflow oven use the concepts of radiation and convection combined. Heat is emitted by ceramic heat element with infrared radiation, but it doesn’t deliver it to a PCB directly. The heat will transfer to a heat regulator first to make heat output even. A convection fan will blow the hot air to an inner chamber. The target PCB can will get heat consistency in any spot.
Related Articles:
Please briefly describe the information you are seeking in the search bar below.






 English
English